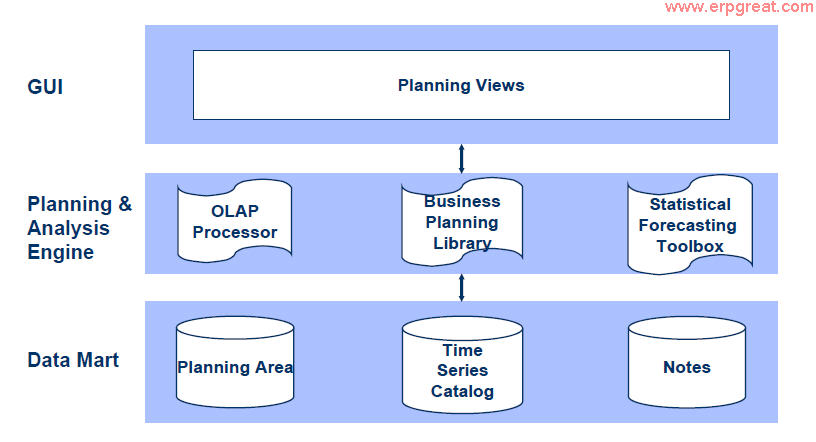
The Demand Planning is composed of three layers:
- Graphical user interface
- Planning and analysis engine
- Data mart
- Performance is of vital importance in any demand planning solution if users are to fully benefit from available information.
- - DP architecture includes several features to ensure high performance:
- Dedicated server.
- Multidimensional data mart based on the star schema that supports efficient use of storage space and of CPU cycles, minimizing query response time.
- Batch forecasting so do not impede online performance.
- The size of the information treated depends on:
- Number of characteristics: many characteristics will let the user more flexibility to define the planning level and to review the information but it makes the system works slower.
- Number of key figures: many key figures will give the user a lot of information related to forecast but it makes the system works slower.
- Number of characteristic combinations: the time consuming for any calculation (e.g. macros) depends directly on the number of characteristic combinations.
- Number of planning versions: two planning versions needs double capacity than one.
- Type and number of temporal periods.
In general we have three types of systems:
1. Planning system (APO)
2. Execution System (R/3)
3. Reporting system (BW)
DP comes under planning system, which is used for accurate forecasts to minimize the inventories, reduce the lead times and finally to have customer delightment.
To have accurate forecast, we need to have some history on which we can forecast(rely). (It is the base for Demand planning). In general, this history of sales will be supplied by Execution systems like R/3 or Main frames.
To make use of this history, initially this will be stored in DataMart (like infocubes). Before this let me explain the architecture in DP.
Data Storage (DataMart) -----> Data Analysis (macros and other planning table calculations) -----> Data Presentation (Planning books and Dataviews)
So any history will initially be supplied to infocubes(data storage) using standard interfaces..
From here we pull the data to planning area. Here we perform some calculations either in the back ground or interactively before forecasting and after forecasting using some macros. Project the forecast using standard forecast techniques or custom tools. After projecting the sales(forecast), user inputs will also be considered interactively in many occasions to calculate the final forecast. This will be done using data views. We come across like profiles and promotions to have accurate forecast. After doing the final forecast, we release it to SNP mid-term planning. DP is long term planning where planned independent requirements are generated. After generating the results, these will be sent back to BW for reporting purpose.
As every company works differently, it will however throw some lights to you on how DP works.